Tailor-Made Functional Polymeric (circular) Materials
Tailor-Made Functional Polymeric (circular) Materials
Hatice Mutlu hatice.mutlu@uha.fr
Developing sustainable platform chemicals and tailor-made polymers
Hatice Mutlu
Environmental challenges, including pollution and the depletion of natural resources, have intensified the demand for renewable materials in recent years across both academia and industry. Consequently, efforts have focused on developing and refining sustainable (green) methodologies that account for the structural diversity of renewable resources and their derived platform chemicals. These advancements aim to unlock new pathways for value creation from renewable feedstocks.Our findings highlight that establishing more sustainable chemical strategies is essential for producing environmentally friendly materials with promising biomedical potential, particularly as innovative cartilage substitutes.
Publications
D. Döpping, J. Kern, N. Rotter, A. Llevot, P. Theato, H. Mutlu,* Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2022, 223, 2100497
J. Kern, H. Mutlu,* D. A. Döpping, N. Rotter, Laryngorhinootologie 2022, 101, 243
D. Döpping, J. Kern, N. Rotter, A. Llevot, H. Mutlu,* ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 13401.
Designing sulfur-based materials for circular chemistry
Hatice Mutlu
Our research focuses on the development of novel sulfur-decorated polymers as next-generation materials aligned with the principles of circular chemistry. We integrate synthetic organic and polymer chemistry with innovative synthetic transformations to establish atom-efficient and sustainable pathways. By leveraging the unique reactivity and tunability of sulfur, we design materials that can outperform or complement conventional carbon- and oxygen-based systems. These sulfur-rich polymers hold strong potential for applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields.
Publications
A. Woodhouse, B. Pektas, C. M. Q. Le, J. A. Garden, H. Mutlu, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2025, DOI : 10.1002/marc.202500056
A. Woodhouse, A. Kocaarslan, J. A. Garden, H. Mutlu, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2024, 45, 2400260
Q. Fu, L. Zhao, X. Luo, J. Hobich, D. Döpping, D. Rehnlund, H. Mutlu,* S. Dsoke,* Small 2024, 2311800
T. Sehn, B. Huber, J. Fanelli, H. Mutlu,* Polym. Chem. 2022, 13, 5965 (This article is part of the themed collection : Chalcogen-containing polymers)
H. Mutlu,* D. A. Döpping, B. Huber, P. Theato,* Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2000695
E. Molle, H. Mutlu,* P. Theato,* Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2100063
H. Mutlu,* P. Theato,* Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, 2000181
H. Mutlu, E. B. Ceper, X. Li, J. Yang, W. Dong, M. M. Ozmen, P. Theato,* Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2019, 40, 1800650.
Engineering precision-functionalized and stimuli-responsive macromolecules
Hatice Mutlu
Our research integrates precise polymer functionalization with advanced macromolecular engineering to access complex, stimuli-responsive, and biomimetic materials. Starting from controlled polymerization of (re)active monomers, subsequent polymer-analogous modifications introduce defined reactive groups along polymer chains, enabling spatially programmed functionality. Using orthogonal reactive handles and multicomponent reactions, we generate highly functionalized block copolymers, end-functional polymers, and modular hybrid systems under atom-economic and sustainable conditions.
Building upon these methods, we develop dynamic and responsive macromolecular systems that emulate features of natural biomolecules. Novel polymer-forming and conjugation chemistries enable the construction of hybrid architectures, including single-chain nanoparticles (SCNPs) and fluorescent self-immolative nanostructures.e-i These systems act as synthetic analogues of proteins, capable of light-induced conformational switching, controlled catalytic behavior, and self-reporting functions.This methodological–functional synergy allows molecular precision to be translated into tunable macroscopic properties. The resulting photo- and redox-responsive polymers, bio-conjugates, and surface-active macromolecules show promise for drug delivery, imaging, biosensing, and adaptive materials. Together, these efforts establish a platform for programmable polymer chemistry, bridging the gap between synthetic control and biological complexity.
Publications
E. Molle, H. Mutlu,* P. Theato,* Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2100063
W. Xue, H. Mutlu, P. Theato,* Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 130, 109660
D. H. S. Ntoukam, H. Mutlu, P. Theato,* Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 122, 109319
J. T. Offenloch, H. Mutlu,* C. Barner-Kowollik,* Macromolecules 2018, 51, 2682
L. D. Thai, T. R. Guimaraes, L. C. Chambers, J. A. Kammerer, D. Golberg, H. Mutlu,* J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 14748
M. S. Akdemir, B. Huber, M. Simian, H. Mutlu,* P. Theato,* ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 6643
M. S. Akdemir, M. Simian, P. Theato,* H. Mutlu,* Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2023, 224, 2200371
S. Sheshachala, B. Huber, J. Schuetzke, R. Mikut, T. Scharnweber, C. M. Domínguez,* H. Mutlu,* C. M. Niemeyer,* Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 3914
J. Hobich, B. Huber, P. Theato, H. Mutlu,* Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2100118.
Self-reporting materials
Hatice Mutlu
Within our efforts in mimicking functions of natural materials, we were not limited only with the synthesis of dynamic light-responsive soft-matter materials with permanent or latent luminescence and fluorescence, we could also show that light is a powerful tool to monitor reactive oxygen species (ROS) in a self-reporting manner. Luminol has attracted scientific interest owing to its low cost and compatibility with a large number of analytes, yet the chemiluminescent (CL) emission generated during the oxidation of luminol is of relatively low intensity. Therefore, a guanidine-based superbase as an efficient CL booster was developed. In contrast to conventional base, organic superbases have allowed the synthesis of monomers for the implementation within multi-functionalized polymers and pave the way for the development of polymeric self-reporting CL-systems.
Moreover, with the aim to reveal that self-reporting polymers has great potential in terms of technical materials applications (e.g., sulfur-based polymers) as well in the area of therapeutic delivery and imaging, high sulfur content polymers were synthesized that could be implemented as a platform material with specified functions (e.g., self-organization, adaptive self-sorting, molecular motion, replication and transcription amongst others) and potential application as protein biochips.
Quite recently, in line with those research activities in the field of sulfur-based polymers, novel class of sulfur-nitrogen based polymers have been synthesized. Importantly, those polymers mimic -amino acid derivatives and thus attract attention by virtue of their potential antibacterial and antifungal activities.
Publications
C. M. Geiselhart, H. Mutlu,* C. Barner-Kowollik,* Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 17290
C. M. Geiselhart, H. Mutlu,* Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2021, 222, 2100057
C. M. Geiselhart, C. Barner-Kowollik,* H. Mutlu,*Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 1732
C. M. Geiselhart, C. W. Schmitt, P. Jöckle, H. Mutlu,* C. Barner-Kowollik,* Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14519
C. M. Geiselhart, H. Mutlu,* P. Tzvetkova, C. Barner-Kowollik,*Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 4213
M. E. Duarte, B. Huber, P. Theato, H. Mutlu,* Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 241
E. Molle, H. Mutlu,* P. Theato,* Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2100063 ;
Circular molecular design : Chemical recycling, repurposing, and hybrid material creation from industrial and domestic waste
Hatice Mutlu
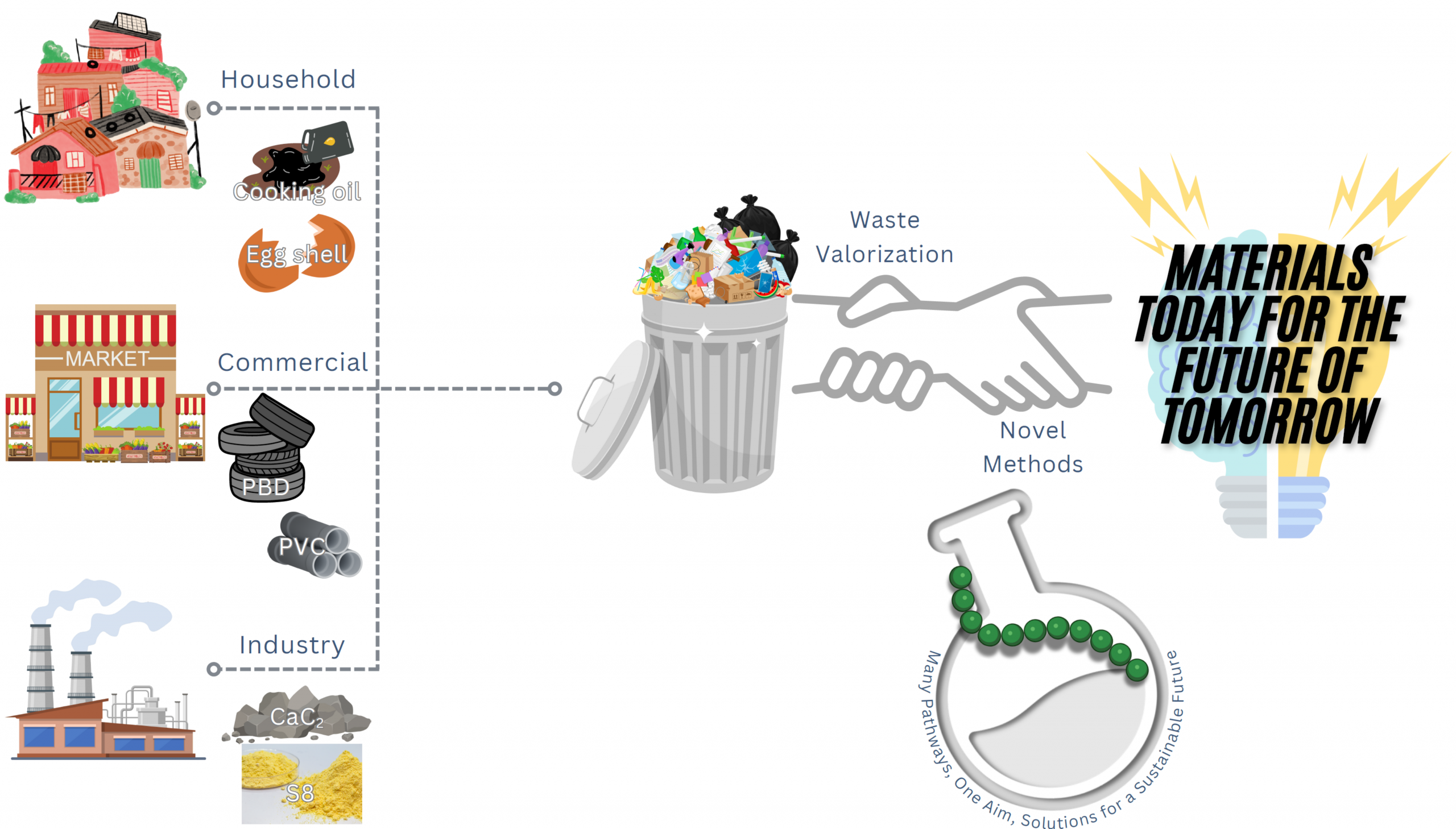
Our research establishes a comprehensive circular chemical platform that bridges recycling, repurposing, and valorization across industrial and domestic waste streams. Beyond conventional upcycling, we develop molecularly guided transformation strategies that convert end-of-life polymers, refinery by-products, and household residues into functional hybrid materials with tailored properties. Through sulfur-based polymer chemistry, we turn elemental sulfur (S₈), a refinery by-product produced in millions of tons annually, into sulfur-rich polymeric frameworks and organic–inorganic hybrids capable of substituting fossil-carbon-based materials. These materials exhibit multifunctionality relevant to energy storage, environmental remediation, and biosensing. In parallel, polybutadiene and polyethylene derivatives are chemically recycled and repurposed into higher-value oligomers and functional materials, extending polymer lifetimes and diversifying their applications.
Furthermore, domestic waste streams such as used cooking oil and eggshell residues (rich in CaCO₃ and minor minerals) are re-engineered into organic matrices with up to 90 wt % sulfur, producing robust hybrid networks with broad utility in catalysis, battery components, and functional composites. Together, these efforts define a materials-chemistry approach to circularity, integrating feedstock re-design, elemental economy, and functional hybrid synthesis to transform underutilized resources into next-generation sustainable materials.
Publications
H. Mutlu,* D. A. Döpping, B. Huber, P. Theato,* Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2000695
Q. Fu, L. Zhao, X. Luo, J. Hobich, D. Döpping, D. Rehnlund, H. Mutlu,* S. Dsoke,* Small 2024, 2311800
J. Jeschke, J. Hobich, H. Mutlu,* Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2025, DOI : 10.1002/marc.202500311
J. T. Offenloch, S. Norsic, H. Mutlu, M. Taam, O. Boyron, C. Boisson, F. D´Agosto, C. Barner-Kowollik,* Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 3633
S. Afonso, H. Mutlu,* Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol., 2025, DOI : 10.1002/ejlt.70018

