Organic-inorganic hybrid materials inspired by talc and saponite like structures
J. Brendlé, L. Dzene
Lamellar clay-like compounds are abundant in nature ; however, they are very rarely pure and may contain secondary phases such as quartz or calcium carbonate, trace elements such as arsenic, or isomorphic subsitutions such as iron that impart coloration, all of which can be problematic depending on the intended application. Hydrothermal synthesis processes allow the production of lamellar compounds with well-defined chemical compositions through careful control of the parameters governing their formation.
Other original and little-explored approach for the synthesis of lamellar compounds is the sol-gel method, in which an organoalkoxysilane (with the formula RSi(OR’)3, R being an organic group and R’ a methoxy or an ethoxy group) is used as the silicon source. The advantages of this process are numerous, as the materials are obtained at room temperature, in a short time, and are directly functionalized via the organic group covalently bonded to silicon.
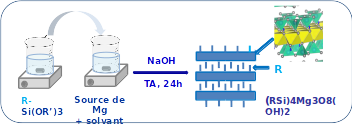
Scheme for preparing organic-inorganic hybrids with a talc-like structure
Current research in this field aims to develop environmentally friendly processes, particularly by using minimally impactful solvents and in smaller quantities, to make the compounds multifunctional, and to expand their fields of application. Particular attention is paid to elucidating formation mechanisms, characterizing compounds using a multi-technique approach, in particular solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and finally to studying structure-property relationships. The fields of application currently being studied are the adsorption of pollutants, the controlled release of active ingredients as well as the preparation of polymer-based nanocomposites, silanized polymers being able to be used as a source of silicon to form organic-inorganic hybrids of talc-type structure.
Publications
In-situ preparation of compounds using silanized mPEG inspired by talc-like structures. L. Dzene, A.-S. Schuller, F. Tidas, S. Rigolet, J. Brendlé, C. Delaite, C. Dalton Transactions, 2023, 52, 8384-8390. DOI : 10.1039/d2dt04016f
Layered Double Hydroxides and LDH-derived materials in chosen environmental applications : a review D. Chaillot, S. Bennici, J. Brendle, Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2021 28, 24375 DOI 10.1007/s11356-020-08498-6
Talc-like hybrids : influence of the synthesis, M. Bruneau ; J. Brendle ; S. Bennici ; L. Limousy, S. Pluchon, New journal of chemistry 2020, 44, 10326 DOI 10.1039/C9NJ06298J
Insights on the influence of the precursors on the sol-gel synthesis of hybrid organic-inorganic saponite-like materials, D. Chaillot, J. Brendle*, S. Bennici, C.R. Chimie 2019, 22,9, 258 DOI 10.1016/j.crci.2019.01.005
Development of a new cathode for the Electro Fenton Process combining carbon felt and organic-inorganic hybrid containing iron, S. M. Miron, J. Brendlé, L. Josien, F. Fourcade, F. Rojas, A. Amrane, L. Limousy, , C.R.Chimie 2019, 22, 238 DOI 10.1016/j.crci.2018.11.012

